Image by fanjianhua on Freepik
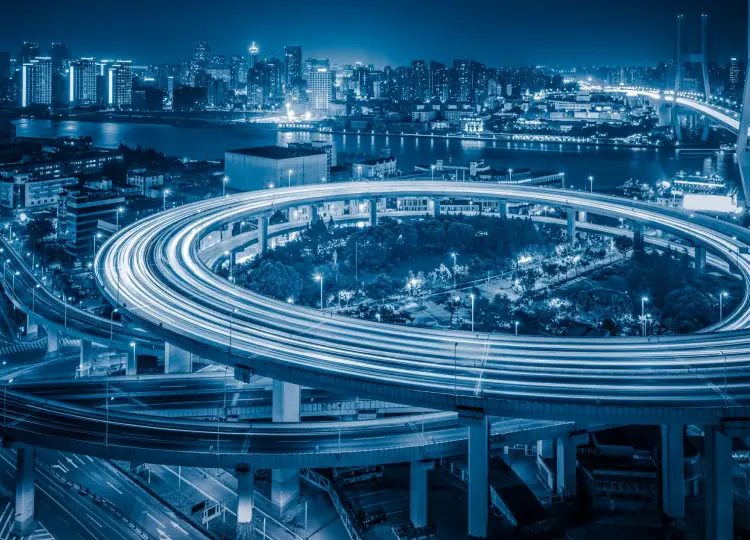
Cities are the heartbeat of modern civilization, attracting millions with promises of opportunity, culture, and community. However, as urban populations surge, cities are facing unprecedented challenges like traffic congestion, pollution, and resource inefficiency. To tackle these issues, cities around the world are turning to technology, specifically the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, to transform into smart cities. In this article, we will explore what smart cities are, how IoT and data are driving this transformation, the benefits and challenges they present, and some notable examples of smart city initiatives.
Understanding Smart Cities
A smart city is more than just a collection of smart devices and data sensors scattered throughout its streets and infrastructure. It's a holistic approach to urban development that leverages technology to enhance the quality of life for its residents while addressing critical challenges. The core components of a smart city include:
1. IoT Infrastructure:
- Sensors, cameras, and connected devices are embedded throughout the city, collecting data on everything from traffic flow and air quality to energy consumption and waste management.
2. Data Analytics:
- Advanced data analytics tools process the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices, extracting valuable insights and patterns that inform decision-making.
3. Connectivity:
- High-speed, reliable internet connectivity is essential for seamless communication between devices and data centers.
4. Sustainability:
- Smart cities prioritize sustainability by reducing energy consumption, promoting green transportation, and optimizing resource use.
5. Citizen Engagement:
- Citizens are actively engaged through digital platforms, allowing them to provide feedback, access services, and participate in decision-making processes.
The Role of IoT in Smart Cities
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the backbone of smart cities. It involves the interconnection of physical objects and devices to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data. In smart cities, IoT is applied in various domains:
1. Transportation:
- Smart traffic management systems use sensors and cameras to monitor traffic flow, reduce congestion, and optimize transportation routes.
2. Public Safety:
- IoT devices enhance public safety by providing real-time information to law enforcement, such as gunshot detection systems and surveillance cameras.
3. Energy Management:
- Smart grids and meters help optimize energy distribution, reduce wastage, and promote energy efficiency.
4. Waste Management:
- Smart bins equipped with sensors signal when they are full, optimizing waste collection routes and reducing unnecessary emissions.
5. Environmental Monitoring:
- Sensors measure air quality, temperature, and humidity, allowing cities to respond to environmental concerns and improve overall health.
6. Water Management:
- IoT sensors monitor water quality and detect leaks, helping conserve this precious resource.
7. Infrastructure Maintenance:
- Sensors embedded in bridges, roads, and buildings detect signs of wear and tear, facilitating proactive maintenance.
Data Analytics: The Brain of Smart Cities
Collecting data is just the first step; the real magic happens when this data is processed and analyzed. Advanced data analytics tools, often powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, are crucial for deriving meaningful insights from the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices. Here's how data analytics contributes to smart cities:
1. Predictive Maintenance:
- By analyzing data from sensors on public infrastructure, cities can predict when maintenance is needed, reducing downtime and costs.
2. Traffic Optimization:
- Traffic data analysis helps cities understand traffic patterns, optimize signal timings, and reduce congestion.
3. Energy Efficiency:
- Data analytics identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption, such as adjusting lighting and heating systems based on usage patterns.
4. Public Safety:
- Crime prediction models use historical data to identify high-risk areas and allocate resources accordingly.
5. Environmental Monitoring:
- Data-driven insights inform pollution reduction strategies and help cities respond to environmental crises.
6. Resource Allocation:
- Data analytics enable efficient allocation of resources, ensuring that services are delivered where they are needed most.
Benefits of Smart Cities
The adoption of IoT and data analytics in urban planning and management offers a multitude of benefits:
1. Efficiency:
- Smart cities optimize resource use, reducing waste and inefficiencies in areas like energy, transportation, and water management.
2. Sustainability:
- The integration of green technologies and data-driven conservation efforts promotes environmental sustainability.
3. Economic Growth:
- Efficient infrastructure and improved quality of life attract businesses and investments, spurring economic development.
4. Safety:
- Smart cities enhance public safety through real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and faster emergency response.
5. Quality of Life:
- Improved services, reduced congestion, and cleaner environments lead to a higher quality of life for residents.
6. Citizen Engagement:
- Digital platforms foster citizen participation in decision-making, making governance more inclusive and responsive.
7. Resilience:
- Data analytics help cities prepare for and respond to natural disasters and other emergencies.
Challenges and Concerns
While smart cities hold immense promise, they also face challenges and concerns that must be addressed:
1. Privacy and Data Security:
- Collecting vast amounts of data raises concerns about privacy and data security. Cities must implement robust measures to protect citizen data.
2. Infrastructure Costs:
- Building and maintaining IoT infrastructure can be expensive, and cities need sustainable funding models.
3. Digital Divide:
- Ensuring that all residents have access to smart city benefits is a challenge, as the digital divide persists in many cities.
4. Vendor Lock-In:
- Relying on a single vendor for IoT devices and data analytics platforms can create vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and competition.
5. Ethical Considerations:
- Decisions made based on data analytics may raise ethical questions, such as those related to algorithmic bias and fairness.
Notable Smart City Initiatives
Several cities around the world have embarked on ambitious smart city projects. Here are a few notable examples:
1. Singapore:
- Singapore's Smart Nation initiative integrates technology into all aspects of urban life, from transportation and healthcare to education and public services.
2. Barcelona, Spain:
- Barcelona's "Superblocks" project transforms city streets into pedestrian-friendly areas while utilizing IoT and data to improve mobility and reduce pollution.
3. Copenhagen, Denmark:
- Copenhagen aims to become carbon-neutral by 2025 through smart solutions like smart traffic lights, bike-sharing systems, and energy-efficient buildings.
4. Songdo, South Korea:
- Songdo is a planned smart city built from the ground up, featuring IoT-based infrastructure and sustainable design principles.
5. Dubai, UAE:
- Dubai's Smart Dubai initiative focuses on improving city services, transportation, and sustainability through data and technology.
Conclusion
Smart cities represent the future of urban living, offering a vision of efficient, sustainable, and inclusive communities. The integration of IoT and data analytics is at the heart of this transformation, enabling cities to address long-standing challenges while improving the quality of life for their residents. However, as smart cities continue to evolve, it's crucial to strike a balance between innovation, privacy, and ethical considerations to ensure that technology serves the best interests of all citizens. The journey to smarter cities is not just about embracing technology; it's about creating a future where cities work smarter for everyone.